The main cause of infertility in women is age. From 25 to 35 years of age, our ovarian reserve decreases by 50%.
The ovarian reserve is the number of eggs that a woman has at a specific time in her life. However, a high ovarian reserve does not mean that there is good oocyte quality.
Meaning of ovarian reserve
Women are born with a finite ovarian supply of approximately one million oocytes. During puberty, the oocytes are reduced to 400,000 - 500,000 eggs. From there, only about 400 - 500 oocytes arrive at monthly ovulation.
The ovarian reserve determines the fertility state of the woman, and the possibility of pregnancy, both naturally and with assisted reproduction procedures.
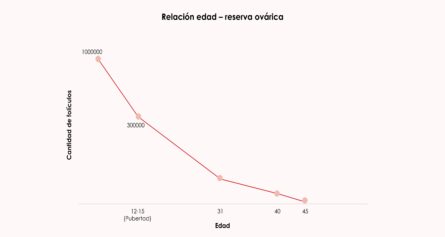
The most fertile time for women is between 25 and 30 years old. From approximately 35 years of age, the ovarian reserve begins to decline, being compromised from 40 years of age until it is completely exhausted, between 45 and 55 years of age.
How can the ovarian reserve be determined?
We can determine the ovarian reserve by performing a gynecological ultrasound in the first days of the cycle (between the 2nd and 5th day). With this simple test we will know the number of antral follicles (ARF) of each ovary. In addition, we perform a hormone analysis female (FSH, LH, Estradiol)
The Antimüllerian Hormone (AMH) also provides information on the ovarian reserve of women. This hormone can be determined through a blood test, regardless of the time of the cycle. This also reflects very well the ovarian reserve.

With the results obtained with these tests we can know what probability of pregnancy we have according to the ovarian reserve.
How to improve ovarian reserve?
There is no treatment to improve ovarian reserve. It is a physiological process determined by age, and therefore, unfortunately, unavoidable.
However, with healthy lifestyle habits (physical exercise, no smoking, avoiding obesity and toxins) and a balanced diet (Mediterranean diet) we can enhance the quality of the ovules.

We can also take foods with antioxidants that can reduce oxidative damage in the ovules, improving their quality and that of the future embryo, thus increasing the pregnancy rate.





No hay comentarios